Sara Rosenbaum's Work
We found 35 items
Include in results:
Model 2. Drug Transporters
Model 1. Introduction to PK and PD
Intravenous Infusion
Download Model
Oral Absorption
Mulitple Bolus Injections Pharmacokinetics
Download Model
Multiple Oral Doses Pharmacokinetics
Download Model
Pharmacokinetics: An IV Injection on a Two Compartment Model
Understanding Restrictive and Nonrestrictive Hepatic Clearance
Multiple Intermittent Infusions Pharmacokinetics
Download Model
Nonlinear Pharmacokinetics and Phenytoin
Download Model
Take the Infusion Challenge
Pharmacokinetics: An IV Injection in a 1-Compartment Model
Sigmoidal Emax Model of Drug Response
Tolerance-Nicotine- Hypothetical Antagonist
Model 15. DDI 3 Reversisble Enzyme Inhibition: Midazolam Fluconazole
Model 20. DDI Drug-Drug Interactions - Pharmacodynamic
Irreversible Drug Effects - Proton Pump Inhibitors
Download Model
Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model
Model 21. Emax Model of Drug Response With an Effect Compartment
Indirect Effect Model 1
Transit Compartment of Drug Action
Download Model
Model 20. DDI Drug-Drug Interactions - Pharmacodynamic
Tolerance- Precursor Pool Model
Download Model
Indirect Effect Model 4
Download Model
Extended Hepatic Cl Model
Model 17. DDI 5 Inhibition of Gut and Hepatic Metabolism
Model 34. Fentanyl Induced Respiratory Depression and its Reversal With Naloxone
Model 13. DDI 1 Time Dependent Enzyme Inhibition
Indirect Effect Model 2
Model 27. Hematological Toxicity of Anticancer Drugs
Operational Model of Agonism
Model 14. DDI 2 Enzyme Induction
Integrated PK-PD Model For Lipoamide
Indirect Effect Model 3
Download Model
Model 16. DDI 4 Time Dependent Enzyme Inhibition Desipramine and Paroxetine
Uploading a Bundle from Zip
Instead of creating bundles, categories, and assemblies one by one, you can upload a single zip file that contains all of your bundle's content. To create your zipped bundle, make a folder with your bundle's name and add subfolders with your categories' names. The folder tree should have the same structure that you want the categories to have in your bundle. Place your assembly .stmx files in the appropriate category folders, then zip your bundle folder and upload it using the Upload Bundle from Zip link above.
Assemblies, Bundles, and Categories
Assemblies are self contained models that demonstrate common ways to connect together building blocks and that can be used as parts of other models. This is analogous to using prefabricated wall and roof pieces to construct a house.
Bundles are groups of assemblies with a common use or theme. For example, a Health Care bundle might contain a variety of assemblies that aid in creating health care models. When you download assemblies from the isee Exchange™, you download an entire bundle, rather than individual assemblies.
Categories are subgroups of assemblies within a bundle. For example, a Health Care bundle might contain a Funding category for assemblies related to the management of hospital funds. All assemblies must be assigned to a category—they cannot be assigned to the root of a bundle.
Assemblies, bundles, and categories can be created and uploaded to the isee Exchange™ via the options on the Manage My Assemblies page. To learn more, visit our help pages, or take our assemblies tutorial.
Sim App (Sim)
An interface that allows users to interact with a model.
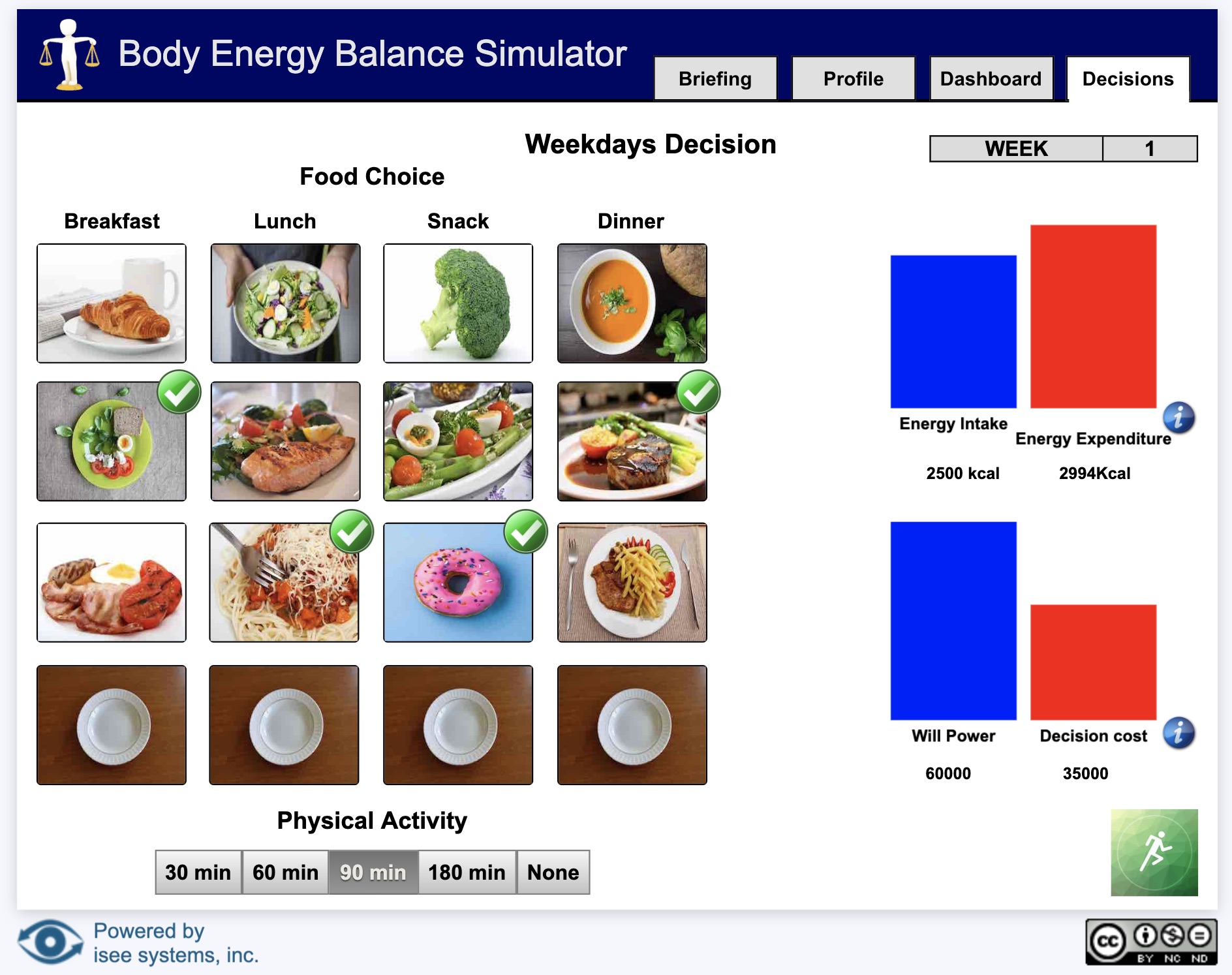
Sim apps allow users to interact with a model using buttons, sliders, knobs, tables, graphs, and storytelling. These interactions help users understand how parts of a system interact.
Interfaces are created by model authors in the Stella desktop software and can be uploaded to the isee Exchange™.
Model
A diagram that represents how elements in a system influence one another.
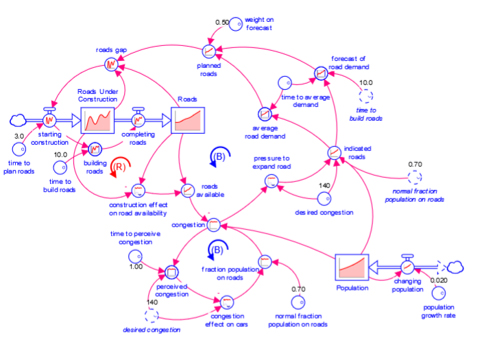
Models are mathematical representations of how elements in a system are connected and interact (e.g., ecosystems, organizations, supply chains). When running models on the isee Exchange™, results can be viewed in output devices like graphs and tables.
Models appear in the isee Exchange™ directory when authors upload them from the Stella® desktop software or create them with Stella Online™.
Causal Loop Diagram (CLD)
A map that represents the feedback structure of a system.
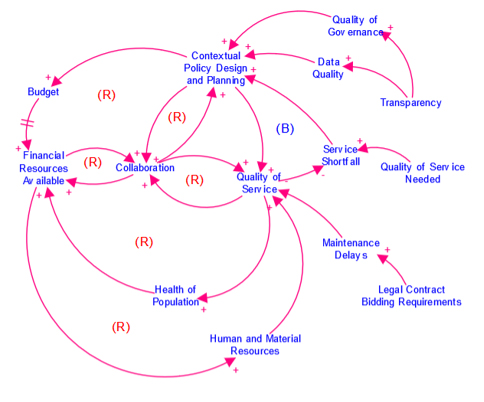
CLDs are high-level maps that represents the feedback structure of a system and easily communicate the essence of a model. They appear in the isee Exchange™ when authors upload them from the Stella desktop software or create them with Stella Online™.